Impacts of a State and Local Bans on New Construction and Upgrades to Fueling Establishments in California
Prepared by Capitol Matrix Consulting for California Fuels + Convenience Alliance (CFCA)
May 2023

Given the emerging movement to ban new or upgraded fueling establishments in California, this report has been commissioned by the California Fuels and Convenience Alliance to analyze (1) the economic contributions of the Fueling and Convenience industry, and (2) the economic impacts that adoption of a statewide ban - or widespread adoption of local bans - would have on the California economy.
Entrepreneurial Opportunities for Small Businesses
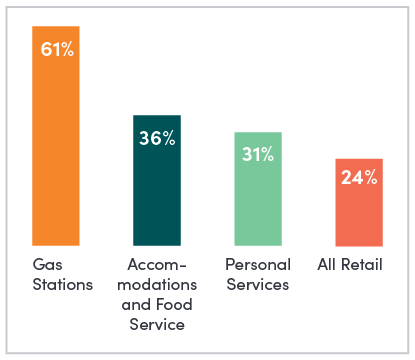
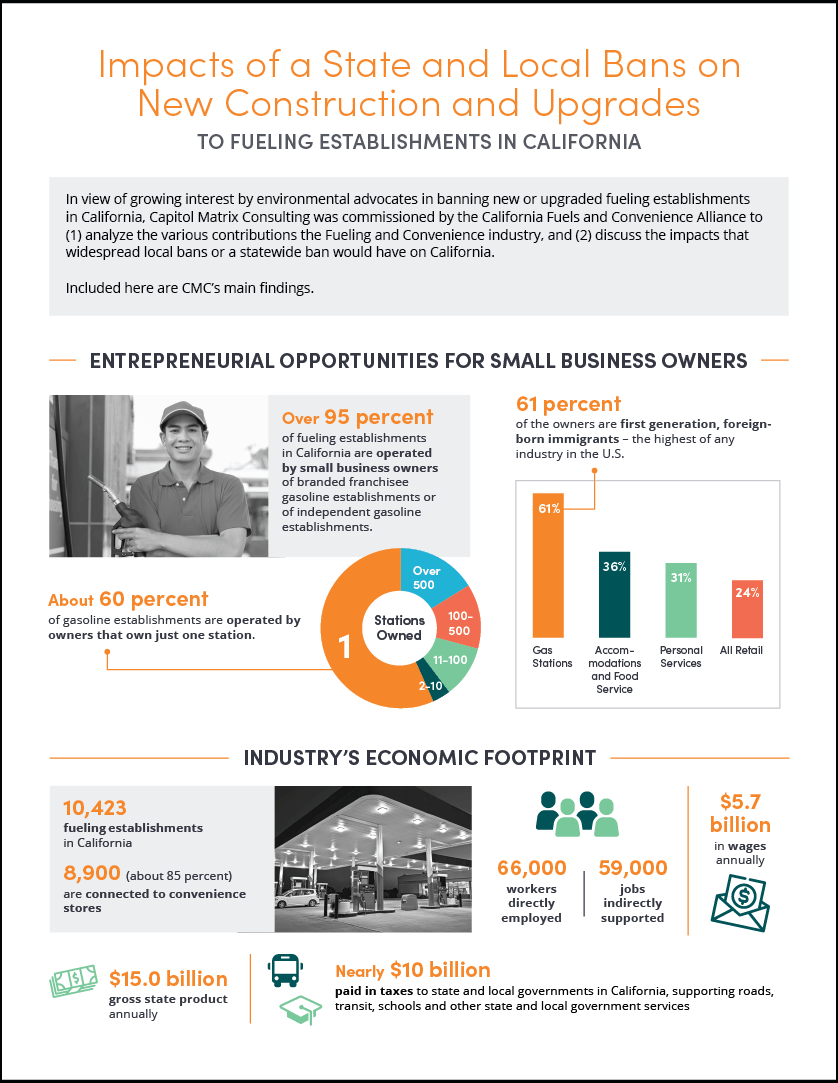
61 Percent
of the owners are first generation, foreign-born immigrants - the highest of any industry in the U.S.

Over 95 Percent
of fueling establishments in California are operated by small business owners of branded franchise gasoline establishments or independent gasoline establishments.
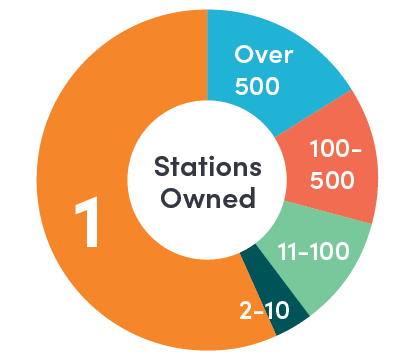
About 60 Percent
of gasoline establishments are operated by owners that own just one station.
Industry's Economic Footprint
10,423
fueling establishments in California
8,900
(about 85%) are connected to convenience stores
$5.7 Billion
in wages annually
$15 Billion
gross state product annually
66,000
workers directly employed
59,000
jobs indirectly supported

Nearly $10 Billion
paid in taxes to state and local governments in California, supporting roads, transit, schools and other state and local government services
Current Benefits to Motoring Public

Provides the motoring public with convenience, reliability, choices of brands and pricing points, and the ability to save time by combining fueling with other purchases.
“Range anxiety” is never a problem, due to the state’s well-developed network of stations.
Future Benefits to Motoring Public
California’s fueling stations are well positioned to dispense:
Hyrdogen
Fuel cell electric vehicles, powered by hydrogen, are a logical alternative for the millions of California families living in apartments where there is a lack of dedicated space and electrical infrastructure for overnight charging of electric vehicles.
Yet as of early 2023 the state had only 63 operating hydrogen dispensing retail stations in place.
Renewable Fuels
Renewable fuels made from agricultural feedstocks, such as soybean or canola oil, sharply reduce net CO2 emissions from transportation and can play a major role in California’s energy transition.
Examples include renewable diesel, gasoline, and natural gas.
Enacted and Proposed Bans on Fueling Station Construction and Upgrades
As of early 2023, 8 cities in Sonoma, Napa, and Marin Counties, as well as the County of Sonoma, have enacted fueling station bans.
Other local governments are considering such bans, and Legislation has been introduced that would require the state to study the feasibility of phasing out existing gasoline stations across the state.
Negative Consequences of Such Bans

Loss of jobs, income and small business ownership opportunities in the fueling and convenience industry.

Loss of fueling option for consumers, adding time and vehicle miles traveled for refueling activities.

Loss of opportunity to convert fueling establishments to dispensers of hydrogen, electrical charging, and other alternative fuels.

Less competition and higher prices for gasoline during the energy transition, especially in growing regions of the state.